Table of Contents
If you owe money to the IRS, you’re likely exploring ways to resolve your tax debt. One of the key forms that can help is Form 433-F, also known as the Collection Information Statement. This form provides the IRS with detailed information about your financial situation, allowing them to assess your ability to pay your debt.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about Form 433-F, including how it works, why it’s important, and how to fill it out effectively.
What Is IRS Form 433-F?
Form 433-F is a financial information statement the IRS uses to determine a taxpayer’s ability to pay their tax debts. It asks for details about the taxpayer’s income, expenses, assets, and debts. IRS agents refer to this form when deciding whether you qualify for certain tax relief programs, like an installment agreement or “currently not collectible” (CNC) status.
Why the IRS Requests Form 433-F

Form 433-F essentially serves as a snapshot of your financial situation. It’s a way for the IRS to evaluate how much you can reasonably pay toward your tax debt each month based on your income, expenses, and other financial commitments. The form is typically required if you owe back taxes and want to set up a payment plan.
Who Needs to Fill Out Form 433-F?
If you’re facing tax debt and considering requesting an installment agreement, the IRS will likely ask you to submit Form 433-F. It’s commonly required for wage earners and self-employed individuals whose expenses exceed their income, as well as those with substantial financial obligations, such as medical expenses, child support, or housing costs.
Difference Between Form 433-F and Other IRS Forms
While there are several IRS forms related to tax debts (such as Form 433-A and Form 433-B), Form 433-F is simpler and is typically used for lower levels of tax debt. The form focuses on monthly living expenses, income, and basic financial details, unlike other forms that require more in-depth information, such as business assets or retirement accounts.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of IRS Form 433-F
Now, let’s take a look at the form itself. You can download it in PDF format from the IRS’s official website or request a copy through the IRS helpline by calling 1-800-829-1040.
Personal and Self-Employment Information
The form starts by asking for your basic details: name, Social Security number, marital status, and address. You must also provide any relevant self-employment information, including the name and nature of your business, your EIN, and the number of employees you have working for you.
Section A: Accounts/Lines of Credit
This section asks for information about all of your financial accounts, including bank accounts, credit cards, and lines of credit. You’ll need to provide information like account numbers, current balances, and whether the account in question is a personal or business account.
Section B: Real Estate
In this section, you’ll list any real estate assets you own, including your primary residence and applicable rental properties. You’ll need to report the purchase price, current market value, and outstanding mortgage balance.
Section C: Other Assets
This section deals with other assets, such as vehicles, business assets, life insurance policies, retirement accounts, and money market accounts. You’ll be asked to provide information about the type and current value of each asset.
Section D: Credit Cards
Here, you’ll list all your credit cards, along with their current balances and credit limits. This will help the IRS better understand your debt obligations and ability to pay.
Section E: Business Information
This section includes questions about accounts receivable to you or any businesses you own. You’ll also be asked to furnish information about your company’s credit card payments.
Section F: Employment Information
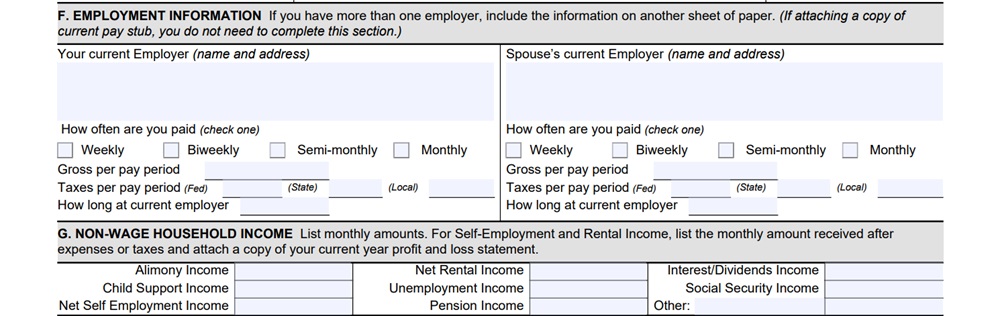
In Section F, you’ll provide details about your employment, including your employer’s name and address and your current gross monthly wages. If you’re self-employed, you’ll need to detail your self-employment income here.
Section G: Non-Wage Household Income
This section asks about other sources of income you may have, such as rental income, child support, mutual funds, or retirement income. Make sure to list all sources of non-wage income accurately to the best of your knowledge.
Section H: Monthly Necessary Living Expenses
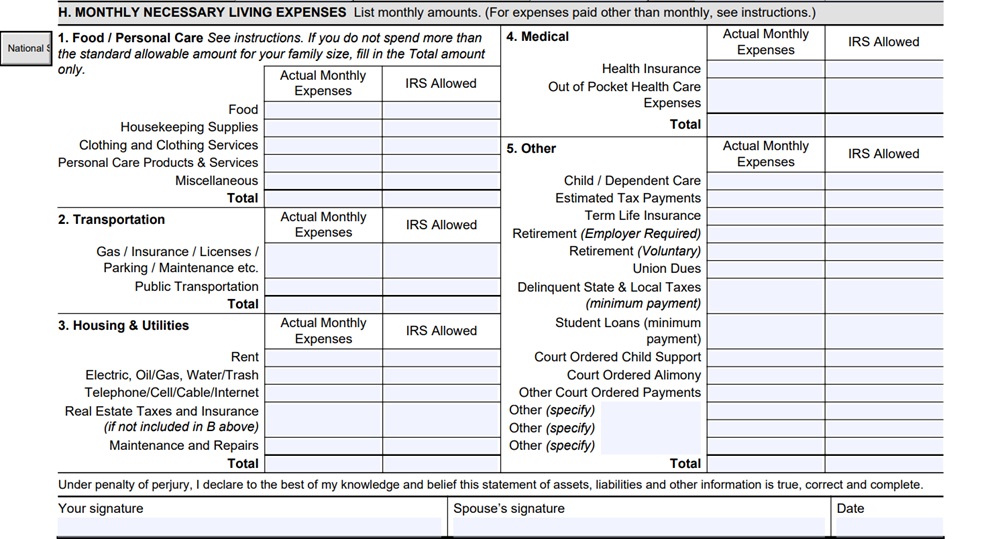
This critical section asks for your monthly expenses, including housing, utilities, food, transportation, health insurance, medical expenses, and child support. The IRS will compare these figures to their allowable expenses to evaluate your financial situation.
Protect Your Rights with a Skilled Tax Attorney
If you’re up against significant tax debt or facing IRS collection efforts, dependable legal representation is crucial. Tax Relief Counsel can offer the knowledge and experience you need to navigate negotiations with the IRS and secure the best possible outcome.
Reach out today to speak with a tax attorney who can defend your rights and help you resolve your tax issues.
Call Me Personally
What Happens After You File Form 433-F?
Once you submit Form 433-F, the IRS will review it and decide on the appropriate next steps.
The agency may offer you an installment agreement, place your account in uncollectible status, or refer your case to a revenue officer. Your information will also be used to assess whether your financial circumstances qualify for a streamlined installment agreement, which could simplify the payment process.
Streamlined Installment Agreement: A Swifter Solution
One of the benefits of submitting Form 433-F is that it can open the door to a streamlined installment agreement.
This program allows you to pay off your tax debt in manageable installments without submitting as much detailed financial information as a standard payment plan. As long as your balance owed is within a certain limit (less than $50,000) and you meet the eligibility criteria, this may be the best option for you.
How the IRS Determines Your Monthly Payment

The IRS will compare your monthly living expenses to their financial standards to judge whether your claimed expenses are reasonable. If your expenses exceed IRS standards, you may be required to reduce certain costs before you can qualify for a payment plan. However, if you’re experiencing financial hardship, the IRS might accept your expenses as-is.
What to Do If Your Expenses Exceed IRS Standards
If the IRS determines that your living expenses exceed their standards, you may need to make some cost-cutting adjustments to qualify for a more favorable payment plan. In cases of extreme financial hardship, a tax attorney can help negotiate on your behalf.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filling Out Form 433-F
Completing Form 433-F incorrectly could lead to complications. Common mistakes include underreporting assets like business credit cards or other investments and failing to disclose all forms of self-employment income.
Take the time to fill out the form fully and accurately and provide supporting documentation for any significant monthly expenses. By doing so, you can ensure that you get the relief you need quickly.
Why You Should Consider Hiring a Tax Professional

Dealing with the complexities of Form 433-F and associated IRS tax relief programs can be overwhelming. In this situation, a tax professional can offer tremendous assistance.
Whether it’s a tax attorney or an enrolled agent, having a professional by your side can help you achieve a favorable outcome. They’ll ensure that your financial information is accurate and present your case in the best possible light.
How to Submit IRS Form 433-F
After filling out the form, you can mail it to the specified IRS address or submit it electronically through the agency’s Online Payment Agreement page. You might also need to send supporting documentation, such as recent pay stubs or bank account statements.
When to Use Form 433-F for a Payment Plan

If you’re considering enrolling in a payment plan or seeking uncollectable status, Form 433-F will be essential for making an appeal to the IRS. The form may be particularly useful if you have limited resources, as it allows the IRS to assess your ability to pay without placing undue financial strain on your day-to-day life.
Get the Relief You Need with IRS Form 433-F
Filing Form 433-F promptly and correctly is an important step toward resolving your financial issues with the IRS. By accurately documenting your income, assets, and expenses, you can open the door to manageable tax relief options tailored to your financial situation.
If you’re unsure how to complete Form 433-F or need assistance addressing your tax debt, don’t hesitate to contact Tax Relief Counsel. We focus on helping individuals and businesses take control of their tax burdens and find practical solutions.
Contact us today to arrange a free consultation, and let us guide you toward financial peace of mind.


