Table of Contents
You might assume that hiring a tax preparer means you’re in the clear if anything goes wrong with your taxes. Unfortunately, even professionals can make mistakes. And when they do, you might be on the hook for penalties.
Whether it’s an honest error or something more concerning, mistakes on a tax return can affect both the preparer and the taxpayer. If you’re under investigation, speak to a tax preparer defense attorney at Tax Relief Counsel. We can explain what you’re up against and advocate for your best interests.
Here, we explore what the tax preparer negligence penalty is, how it can affect you, and what both taxpayers and tax preparers need to know to avoid costly consequences.
What Is the Tax Preparer Negligence Penalty?

Tax preparer negligence penalties are fines or other punishments imposed on tax professionals. The IRS might assess these penalties when a tax preparer negligently or improperly files a return or when they provide tax advice that results in a client underpaying their taxes.
Some examples of tax preparer negligence include failing to properly calculate tax deductions or omitting required information.
Tax preparer negligence can lead to serious financial consequences for both the taxpayer and the preparer. If the IRS determines that the preparer’s actions were reckless or intentional, the penalties for the tax preparer are more severe and may include prison time.
Who Qualifies as a Tax Preparer?
A tax preparer is defined by the IRS as anyone who is paid to prepare or assist in preparing someone else’s income tax return. This includes tax professionals like accountants, enrolled agents, or attorneys. Even someone who only offers advice on tax matters can be considered a tax preparer if their advice directly influences a client’s tax return.
Who Is Liable for Tax Preparer Penalties?
Tax preparers are directly liable for these penalties. However, taxpayers can also be affected. If your preparer makes a mistake on your tax return, you’ll be responsible for paying any additional taxes, penalties, and interest that result from that mistake.
In some cases, the IRS may hold both the taxpayer and the preparer accountable. This may happen if the agency believes you colluded with each other in order to underpay taxes.
Common Causes of Tax Preparer Penalty
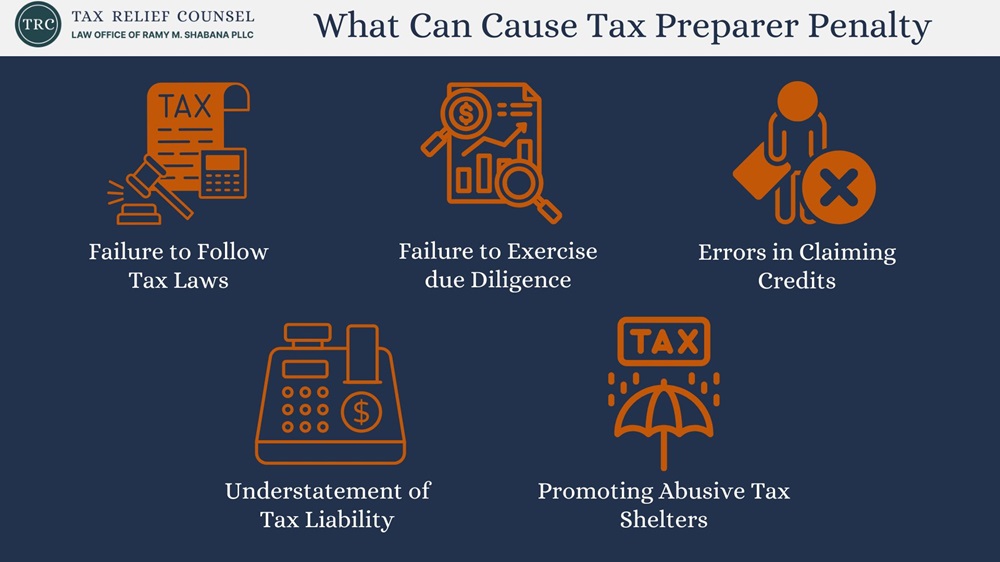
There are several reasons why a tax return preparer might face negligence penalties:
- Failure to follow tax laws: If the tax preparer ignores relevant tax laws or fails to stay up to date with changes, they can easily make mistakes on a return.
- Failure to exercise due diligence: This includes not thoroughly verifying the taxpayer’s information or failing to request the proper documents.
- Errors in claiming credits: Incorrectly applying for credits, like the earned income tax credit (EITC) or the additional child tax credit (ACTC), can lead to penalties.
- Understatement of tax liability: A tax preparer might incorrectly reduce the taxpayer’s liability through improper deductions or misreporting of income.
- Promoting abusive tax shelters: If a preparer encourages clients to participate in tax shelters to illegally lower their tax burden, they will be subject to penalties.
The IRS lists specific fines and other consequences for tax preparer negligence and misconduct on its website.
Negligence vs. Willful Misconduct
When determining penalties for tax preparers, the IRS distinguishes between negligence and willful misconduct.
Negligence generally involves a lack of care, where the preparer makes a mistake due to oversight or ignorance.
In contrast, willful or reckless conduct implies that the preparer knowingly or intentionally violated tax laws. This type of conduct might include making false claims or promoting abusive tax shelters. Along with financial penalties, tax preparers can face felony charges and imprisonment for these crimes.
Common Examples of Tax Preparer Negligence
Tax preparer negligence can take many forms, but some of the most common include:
- Miscalculating deductions or credits such as the EITC
- Underreporting a client’s income
- Filing under the wrong household filing status
- Failing to attach required tax documents
- Misreporting income from multiple sources
- Providing incorrect advice based on outdated tax laws
These mistakes might seem minor, but they can result in significant penalties for the tax return preparer and the taxpayer.
What Are the Penalties for Tax Preparer Negligence?

The penalties for tax preparers vary based on the severity of the offense. Section 6694 of the Internal Revenue Code outlines the consequences for unreasonable errors and willful misconduct. Other sections of the code address less serious mistakes.
These are some of the most common penalties a tax preparer could face.
Failure to Exercise due Diligence Penalty
Tax preparers must meet due diligence requirements, especially when preparing returns that claim certain credits like the EITC or the AmericaOpportunity Tax Credit. If the IRS determines that the tax preparer failed to conduct due diligence, the agency can impose a penalty for each return the tax preparer handled.
Negligent or Intentional Understatement of Tax Liability Penalty
If the preparer negligently understates a taxpayer’s liability, the IRS can impose a penalty of $1,000 per return or 50% of the preparer’s fee, whichever is higher.
A tax preparer who intentionally or recklessly disregards IRS regulations to understate a client’s tax liability can face higher fines. They could pay $5,000 per return or 75% of the fee they charged.
Fraud or False Statement Penalty
When the tax preparer knowingly provides false information or commits tax fraud, they could be charged with a federal crime. The preparer could also be barred from practicing. Someone convicted of tax fraud could spend up to three years in prison.
Facing IRS Penalties for Tax Preparer Negligence? Let Us Defend Your Rights.
Are you being targeted by the IRS because your tax preparer was negligent? The experienced attorney at Tax Relief Counsel is ready to build your defense. Contact us today to discuss your case and protect your financial future.
Call Me Personally
How to Avoid Tax Preparer Penalties
Tax professionals should strictly adhere to IRS guidelines to avoid financial penalties. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Exercise due diligence: Always double-check tax returns for accuracy, especially when claiming credits like the EITC or the ACTC.Stay up to date: Keep informed about new tax laws to ensure you’re providing accurate tax advice.
- Document everything: Maintain detailed records of how you prepare each tax return.
- Verify income and deductions: Don’t rely on estimates or guesses; request documentation to support any income or deductions claimed on the return.
Never take a client’s word for it without asking for supporting documentation. Conducting due diligence can protect both you and your client.
What Is the Preparer Tax Identification Number Requirement?
To promote accountability and make it easier to trace the actions of tax professionals, the IRS issues a Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN) to anyone who is paid to prepare tax returns and similar documents. A paid tax preparer must include their PTIN on all returns they assist with or prepare. Failure to do so can lead to additional penalties.
Tax Preparer Liability and Civil Penalties
Tax preparer liability extends beyond IRS fines. If a tax preparer’s negligence or reckless behavior leads to an audit or further IRS action, the preparer can face civil penalties. A client may hold their tax preparer accountable in court, especially if the error results in significant penalties and interest.
What Is Reasonable Cause and Good Faith?
Sometimes mistakes happen despite a tax preparer’s best efforts. In cases where the preparer can demonstrate reasonable cause and acted in good faith, the IRS may waive penalties. However, this defense may require evidence that the preparer relied on incorrect information provided by the client or that there were other unusual circumstances.
What to Do If You Receive an IRS Notice

If you’re a tax preparer and you receive an IRS notice for penalties, review the notice thoroughly. Ignoring it can result in additional penalties and further action by the IRS.
The notice should have instructions about what to do next. If you’re unable to resolve the issue easily, consider consulting an experienced tax attorney.
How to Protect Yourself as a Taxpayer
As a taxpayer, it’s crucial to ensure your tax return preparer is qualified and follows proper procedures. Here are a few tips to protect yourself from preparer errors:
- Verify your preparer’s credentials: Ensure your tax preparer has a valid PTIN and other relevant qualifications.
- Review the return before filing: Don’t just sign the tax return without reviewing it — make sure the numbers look correct and all necessary documents are attached.
- Ask questions: If something on your return doesn’t seem right, don’t hesitate to ask your preparer for clarification.
Even though you’ve trusted someone else to handle your taxes, you’re ultimately responsible for paying them.
What Should You Do If Your Tax Preparer Makes an Error?
If you discover that your tax preparer made a mistake on your return, the first step is to correct it as soon as possible. You may need to file an amended return or contact the IRS directly to resolve the issue. It’s essential to address the problem quickly to avoid additional penalties or interest.
Avoid Tax Preparer Negligence Penalties and Protect Your Finances
The tax preparer negligence penalty is unwelcome for both taxpayers and preparers, but it’s avoidable with proper care and due diligence. By following IRS guidelines, keeping up with tax law changes, and ensuring every tax return is accurate, tax preparers can reduce their risk of facing penalties.
For taxpayers, selecting a qualified preparer is equally important. Taxpayers who encounter mistakes can seek assistance from a tax attorney for help resolving the matter quickly and efficiently.
If you’re facing IRS penalties due to tax preparer negligence, we can help. Tax Relief Counsel is here to defend your rights. Contact us today and let our experienced tax attorney handle the rest.


