Table of Contents
Receiving a letter from the IRS is rarely a cause for celebration.
That official-looking envelope in your mailbox can trigger a wave of anxiety, leaving you wondering, “What do I owe now?” or, “Did I do something wrong?” It’s no wonder that dealing with the IRS is a common source of stress for taxpayers, especially those facing a complicated tax situation or potential audit.
Before you let those worries take over, however, take a breath. Understanding the types of IRS letters and notices — and knowing what actions to take to follow up on them — can help you respond to these communications with more confidence.
Why Does the IRS Send Letters?

The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sends out an enormous volume of letters and notices to taxpayers each year. These communications serve various purposes, all aimed at ensuring compliance with tax laws and proper management of tax accounts.
Here are some of the reasons you might receive a letter from the IRS:
Request for Information
The IRS might request additional information or documents to verify details on your tax return or clarify discrepancies. Sometimes, this might be to verify your eligibility for a tax credit or to confirm income information the agency has received from other sources.
Account Update
Some notices might provide updates on your tax account, such as changes to your balance due, confirmation of payments received, or adjustments to your refund amount. You might also receive a notice if the IRS has applied part or all of your refund to offset other tax debts or outstanding federal debts, such as student loans.
Notification of Balance Due
If you owe taxes, you’ll receive a balance due notice outlining the amount you owe and instructions for making payments.
Notification of Refund
In the best-case scenario, the IRS might send you a letter confirming a refund, explaining the amount you’re due and when to expect it.
Proposed Changes to Your Return
If the IRS proposes adjustments to your tax return that could impact your tax liability, they’ll notify you through specific letters. This might involve a change to your income, filing status, or deductions.
Notification of Intent to Take Action
In more serious situations, the IRS sends letters outlining its intended actions if tax debts remain unpaid. These might include filing a federal tax lien, levying assets (seizing property or wages), or initiating other collection efforts.
Understanding why the IRS is sending you a letter is the first step to taking the appropriate action.
Identifying Your IRS Letter or Notice: What to Look For
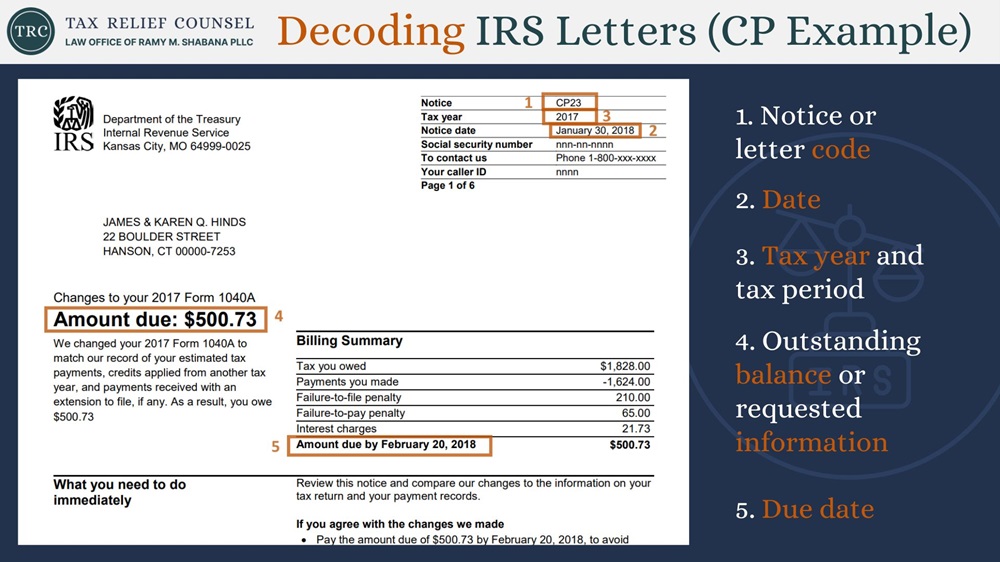
It’s important to read the letter or notice you’ve received carefully before you panic. Each communication will include key identifying elements that will help you decode it.
Here’s what to look for:
Notice or Letter Code
In the upper right corner, you’ll find a unique code, often starting with “CP” or “LTR,” followed by a series of numbers. These codes provide a clue as to the letter’s purpose.
Date
Take note of the date the letter was issued. You’ll need to know it in order to meet deadlines for responses or payments.
Tax Year
The letter will specify the tax year it pertains to (e.g., 2023) so you can easily locate the corresponding tax return. This might be for the current tax year or a prior tax year.
Tax Period
For notices related to employment or business taxes (like quarterly payroll tax filings), the tax period in question will be identified.
Tax Period Shown
Some notices might reference a specific date range or period within the tax year.
Outstanding Balance
If you owe money to the IRS, the notice will state the amount due.
Requested Information
If the IRS is seeking specific documents, tax records, tax information, or additional information, the body of the letter will outline those requests.
Due Date
Pay close attention to any deadlines mentioned in the letter for responding, making payments, or taking other actions. There could be consequences if you fail to take appropriate action by these deadlines.
Once you understand these key elements, you’ll be better equipped to interpret the letter’s content and respond accordingly.
Common IRS Notices

The IRS uses a vast array of notice and letter codes to communicate with taxpayers, each of which has a specific purpose. Here’s an overview of the most common types of IRS letters:
CP Notices
CP notices often relate to individual income tax returns or taxpayer accounts. They can range from simple balance-due reminders to more complex notices about proposed tax changes. Some of the most frequently sent CP notices include:
CP14: Notice of Balance Due
This is one of the most common notices. If you owe taxes and haven’t paid the amount by the due date, you’ll receive a CP14 notice outlining your balance and payment options, as well as the potential consequences of non-payment.
If you’re unable to pay the full balance, the IRS might allow you to set up a payment plan, also known as an installment agreement, to pay off your debt over time.
CP2000: Underreporter Inquiry
If the IRS receives income information from your employer, bank, or other sources that doesn’t match what you reported on your return, they’ll send you a CP2000. This notice will outline the discrepancies, propose adjustments to your original return, and calculate the potential additional tax or refund owed.
CP21B: Notice of Requested Changes
This notice serves as confirmation that the IRS has made the changes to your tax return you requested for a specific tax year. If you get a CP21B in the mail, you can expect to receive a refund check within two to three weeks.
Math Error Notices
While not technically a distinct category, these notices are often included with CP letters. The IRS might send a notice (for example, a CP2000) that identifies a simple mathematical error on your original return. The notice will explain the error and how it affects your refund or balance due.
Notice of Federal Tax Lien Filing (LT11)
An LT11 notice is serious business. It means the IRS is taking steps to secure their claim to your property (real estate, vehicles, etc.) due to a significant unpaid tax debt. This notice typically follows multiple ignored balance-due notices and is a strong indicator that the agency intends to escalate its collection actions.
Notices Regarding Tax Credits
The IRS might use different notices to address credits claimed on your tax return.
For example, the agency might send a CP75 or CP75A notice if there are questions or adjustments related to the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) claimed on your return. They could be requesting additional information to verify your eligibility or explaining a reduction in the credit amount.
If the IRS determines that you’re ineligible for a tax credit you claimed, they’ll adjust your return accordingly.
Need Help Understanding a Specific Notice or Figuring Out Your Next Steps?
Ramy Shabana, seasoned tax attorney and founder of Tax Relief Counsel, can help you understand your IRS notice and take prompt action to stay in the clear. Contact us today to schedule a consultation.
Call Me Personally
Other Important IRS Notices
Beyond CP notices, the IRS may send a wide range of other notices to address specific tax matters. Here are just a few:
Audit Notices
While any IRS letter can be nerve-racking, an audit notice often triggers high levels of stress for taxpayers. If your tax return has been selected for examination, the IRS will send you one of the following types of audit notices with further details:
Letter 566: Examination of Income Tax Return
This letter formally informs you of the audit. It specifies the tax year being looked at, the type of audit (correspondence or field audit), and the information and documentation you’ll need to provide.
CP2000
As mentioned, a CP2000 notice can also be considered an audit notice, as the IRS is proposing changes to your return based on their findings.
Collection Notices
When a tax debt remains unpaid, the IRS ramps up its collection efforts. These letters become increasingly urgent, culminating in potential asset seizures:
- CP501 — Reminder notice: A first reminder that you have an unpaid tax balance.
- CP503 — Second notice: A follow-up reminding you of the outstanding amount, indicating that the IRS hasn’t received payment.
- CP504 — Final notice before levy: A final warning that the IRS will begin levying your assets if you don’t pay or make other arrangements.
- LT11 — Final notice of intent to levy: Confirmation of the IRS’s plans to initiate a levy, which might involve seizing funds from your bank account or garnishing your wages.
The LT11 notice also explains your right to request a collection due process (CDP) hearing to appeal the levy.
Statutory Notice of Deficiency (90-Day Letter)
Also known as a CP3219N, a Notice of Deficiency is sent when the IRS has completed an audit and proposes significant changes to your tax return. These changes often result in an increase in your tax liability (a larger balance due) or a reduction in your expected refund.
The 90-day letter is a critical notice, as it gives you 90 days from the date indicated on the letter to either pay the proposed deficiency or file a petition with the Tax Court.
If you disagree with the proposed changes, you can ask the Tax Court to review your case. You should consider taking this path if you believe you have grounds for an appeal.
Notices Related to Federal Employment Tax or Excise Taxes
Businesses often receive various notices from the IRS related to federal employment taxes (payroll taxes) or, less commonly, excise taxes. They may include:
Notice 941: Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return
This form (and associated notices) covers taxes withheld from employee wages, Social Security taxes, and Medicare taxes. The IRS might send balance-due notices, penalty notices for late filing or late payments, or requests for additional information regarding your 941 filings.
Notice CP250A: Change of Tax Filing Requirement
This notice is meant to inform business owners of changes to their federal employment tax filing requirement, which happens when their annual employment tax liability exceeds $1,000.
What to Do When You Receive an IRS Letter

No matter what type of letter or notice arrives in your mailbox, it’s critical not to ignore it. The IRS has significant power to collect unpaid taxes. While some letters might be simple reminders or requests for information, others could be warnings of impending collection actions.
Here’s a breakdown of the steps you should take to address your recent IRS notice:
Don’t Ignore It
The IRS won’t leave you alone just because you ignore its letters. In fact, doing so will only make things worse. Your best bet is to face the issue head-on.
Read the Notice Carefully
Take the time to review the notice in its entirety. Pay close attention to the following:
- Notice or letter code: Indicates the nature of the tax issue.
- Date: The date the notice was sent.
- Tax year: The year the notice pertains to.
- Tax period: May be applicable for business taxes.
- Outstanding balance: What you owe the IRS.
- Requested information: The specific documents, tax records, or information you need to provide.
- Due date: The deadline to respond or make a payment.
These elements will tell you what the notice is about and what you need to do to resolve the underlying issue.
Gather the Necessary Information or Documents
If the IRS is requesting specific information or forms, locate them promptly and double-check them for accuracy prior to submission.
Respond to the IRS
Whether you’re providing information, paying your balance, or making a request, it’s essential to reply to the IRS by the due date specified in the notice.
Consider Your Options
Depending on the type of notice you receive, you may have the option to:
- Make a payment if you agree with the amount due.
- Request a payment agreement to set up a payment plan.
- Appeal a determination if you believe a tax adjustment is incorrect.
- Request a CDP hearing if the IRS intends to levy your assets.
Make sure to read the included instructions carefully to better understand what steps you’ll need to take.
Spotting IRS Scams

Not all communications that appear to originate from the IRS are legitimate. Here are some red flags that can help you identify potential scams:
Unexpected Contact
The IRS initiates most contact through regular mail. Be wary of unexpected calls, emails, or text messages claiming to be from IRS agents. If you receive an unusual call, don’t give out any personal or financial information.
Threatening Language
The IRS will never threaten you with arrest, legal action, or deportation if you don’t pay immediately. These are tactics scammers use to intimidate their victims into handing over money.
Demands for Specific Payment Methods
Scammers often pressure taxpayers to make payments using gift cards, prepaid debit cards, wire transfers, or cryptocurrencies. The IRS provides a list of legitimate payment options, which you can find on the agency’s website.
Requests for Personal Information via Email or Phone
The IRS generally won’t request sensitive personal information, such as your Social Security number or bank account details, over email or phone. Being asked for this information over these channels should give you pause.
What to Do If You’re Targeted for a Scam
If you suspect you’ve been targeted by an IRS scam or have received a suspicious letter or notice, here’s what you should (and shouldn’t) do:
Don’t Engage with the Scammer
If you’re on the phone, hang up as soon as your suspicions arise. If you’ve received a link via email or text message, refrain from clicking it.
Report the Scam to the IRS
You can report the scam online using the IRS’s “Report Phishing and Online Scams” page. You can also contact the Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration (TIGTA) at TIGTACommunications@tigta.treas.gov.
Contact a Tax Professional
If you’re ever unsure about the legitimacy of an IRS communication, it’s a good idea to reach out to a qualified tax professional. They can help you verify the notice, protect your rights, and advise you on the best course of action.
When to Seek Professional Help

While you can handle some IRS notices on your own, seeking guidance from a tax professional is crucial under the following circumstances:
- You’re unsure what the notice means or what actions to take.
- You disagree with the IRS’s assessment, such as proposed tax changes or penalties.
- You’re facing a complex tax issue, such as one that requires you to discuss your tax liability or refund with a former spouse.
- You need help responding to a 90-day letter, understanding your appeal options, or preparing for a CDP hearing.
Issues like these are best tackled under the supervision of a knowledgeable tax professional, who will be familiar with the relevant tax laws and IRS procedures needed to resolve the matter.
How a Tax Lawyer Can Help
When you work with the dependable tax professionals at Tax Relief Counsel, you’ll enjoy the following advantages:
- Knowledgeable interpretation: We’ll break down complex IRS language into clear, easily understandable terms, explaining the nuances of your notice.
- Strategic guidance: Our team will help you develop the most effective response strategy based on your individual tax situation.
- Effective communication: We’ll handle all communication with the IRS on your behalf, meeting key deadlines, submitting accurate responses, and protecting your rights.
- Peace of mind: Dealing with the IRS can be stressful. We’ll take the burden off your shoulders, allowing you to focus on other important aspects of your life.
Contact us for a free, private consultation today, and let us put our experience to work for you.
IRS Notice Codes: A Quick Reference Guide
To help you identify and address your specific notice, we’ve provided a comprehensive table detailing the many types of IRS notices and what they mean:
| Notice Code | Description | Topic Category |
|---|---|---|
| CP01 | Identity theft indicator placed on your account | Identity Theft |
| CP01A | Provides an Identity Protection Personal Identification Number (IP PIN) | Identity Theft |
| CP01C | Acknowledgment of identity theft documentation; account marked with indicator | Identity Theft |
| CP01H | Unable to process return; SSN belongs to deceased person | SSN |
| CP01S | Identity theft claim received; will contact with refund or request for information | Identity Theft |
| CP02H | Balance due because of amending return to show Hurricane grant | Balance Due |
| CP03C | May need to file a form to report ownership change for first-time homebuyer credit | Credit |
| CP04 | Deployment to combat zone; need to file return | Filing |
| CP05 | Holding refund for review of treaty benefits and Schedule A deductions | Deductions |
| CP05A | Examining return; need documentation | Verification |
| CP05B | Holding refund; need to verify income | Refund |
| CP06 | Audit of return for premium tax credit; holding refund | ACA |
| CP06A | Audit of return for premium tax credit; need documentation | ACA |
| CP07 | Holding refund; need to review treaty benefits or Schedule A | Deductions |
| CP08 | Possible eligibility for Additional Child Tax Credit (ACTC) | Refund |
| CP09 | Possible eligibility for Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) | Refund |
| CP10 | Change made to return affects estimated tax payments for next year | Estimated tax credit |
| CP11 | Changes made to return result in balance due | Balance due |
| CP11A | Changes to return (EITC) result in balance due | Balance due |
| CP11M | Changes to computation of Making Work Pay Credit | Return error |
| CP12 | Changes made to correct return | Refund |
| CP12A | Changes to correct EITC on return | EITC |
| CP12E/12F | Changes to correct miscalculation on return | Return error |
| CP12M | Changes to computation of Making Work Pay/Government Retiree Credits | Return error |
| CP12R | Changes to computation of Rebate Recovery Credit | Return error |
| CP13 | Changes to return result in a balance of zero | Zero balance |
| CP13A | Changes to return due to error with EITC | Zero balance |
| CP13M | No tax liability or refund after adjustments for Making Work Pay Credit | Zero balance |
| CP13R | Changes to return involving Recovery Rebate Credit result in zero balance | Zero balance |
| CP14 | Balance due on unpaid taxes | Balance due |
| CP14A/B/C/D/E | Balance due on unpaid taxes | Balance due |
| CP14H | Balance due on Shared Responsibility Payment (SRP) | ACA |
| CP14I | Penalties charged for not taking out IRA minimum | Penalty |
| CP15B | Penalties charged for unpaid employment or excise taxes | Penalty |
| CP15H | SRP assessment due to income change | ACA |
| CP16 | Changes made to return affect refund, offset for other tax debts | Refund |
| CP18 | Incorrect claiming of deductions/credits | Balance due |
| CP19 | Amount of tax owed increased due to incorrect deductions/credits | Deductions |
| CP20 | Refund less than expected due to incorrect deductions/credits | Deductions |
| CP2000 | Underreporter inquiry | Underreporter |
| CP2005 | Accepted information provided; case closed | Underreporter |
| CP2006 | Accepted information provided; awaiting determination | Balance due |
| CP2057 | Need to file amended return | Amended return |
| CP21A | Changes requested to return result in balance due | Balance due |
| CP21B | Changes requested to return result in a refund | Refund |
| CP21C | Changes requested to return, resulting in no change to balance | Zero balance |
| CP21E | Changes made to return after examination | Review |
| CP21H | Change to SRP | Balance due |
| CP21I | Changes to IRA taxes resulting in a balance due | Balance due |
| CP22A | Requested changes to return result in balance due | Balance due |
| CP22E | Changes due to recent audit result in balance due | Balance due |
| CP22H | Changes to return also change SRP | Balance due |
| CP22I | Changes to IRA distributions resulting in balance due | Balance due |
| CP23 | Balance due from difference in estimated tax payments and amount credited | Balance due |
| CP24 | Changes to return due to difference between estimated tax payments and amount posted to account | Refund |
| CP24E | Overpayment credit due to difference between estimated tax payments and credited amount | Refund |
| CP25 | Zero balance due to changes in estimated tax payments | Zero balance |
| CP2501 | Payment information discrepancy | Underreporter |
| CP2566 | No tax return received; tax calculated based on income info | ASFR |
| CP2566R | No response to CP63 (holding refund); tax calculated based on income info | ASFR |
| CP27 | Potential eligibility for EITC | Review |
| CP30 | Penalty charged for underpayment of estimated tax | Penalty |
| CP301 | Confirmation of visiting IRS website and registering for service | Identity theft |
| CP30A | Penalty reduced or removed for underpayment of estimated tax | Penalty |
| CP32 | Replacement refund check sent | Refund |
| CP3219A | Information differs from return | Deficiency notice |
| CP3219N | No tax return received; Notice of Deficiency (90-day letter) | Deficiency notice |
| CP32A | Call to request refund check | Refund |
| CP39 | Refund from you or spouse used to pay past-due tax debt | Balance due |
| CP42 | Refund amount changed due to application to taxes owed | Refund |
| CP44 | Delay in processing refund due to taxes owed | Balance due |
| CP45 | Overpayment could not be applied to estimated tax as requested | Overpayment |
| CP49 | Refund used to pay tax debt | Overpayment |
| CP501 | Balance due on tax account | Balance due |
| CP501H | Balance due on SRP account | ACA |
| CP503 | Unpaid balance on tax account; no response to previous notice | Balance due |
| CP503H | Unpaid balance on SRP | ACA |
| CP504 | Unpaid balance on account; final notice | Balance due |
| CP515I | Balance due; unfiled prior-year tax return | Balance due |
| CP516 | Missing prior tax return(s); reminder | Filing |
| CP518I | Missing prior tax return(s); final notice | Filing |
| CP51A | Balance due on Form 1040/1040A/1040EZ | Balance due |
| CP51B | Refund due on Form 1040/1040A/1040EZ | Refund |
| CP51C | Zero balance on account after computing Form 1040/1040A/1040EZ | Zero balance |
| CP52 | Correction to claimed self-employment taxes | Self-employment tax |
| CP521 | IRS installment payment due | Installment agreement |
| CP523 | Installment agreement defaulted; intent to terminate and levy assets | Levy |
| CP523H | Intent to terminate installment agreement | Installment agreement |
| CP53 | Direct deposit of refund unsuccessful; reissue sent by mail | Direct deposit |
| CP53A | Direct deposit unsuccessful; research in progress; reissue in 8–10 weeks | Direct deposit |
| CP53B | Direct deposit unsuccessful; research in progress; reissue in 8–10 weeks | Direct deposit |
| CP53C | Direct deposit unsuccessful; research in progress (questionable payments) | Direct deposit |
| CP53D | Direct deposit rejected; issuing paper check instead | Direct deposit |
| CP547 | Receipt of Form 2848, Form 706, or Tax Information Authorization; Centralized Authorization File (CAF) number assigned | CAF |
| CP54B | Different name/ID number on return; need more information | Name/SSN |
| CP54E | Different name/ID number on return; need more information | Name/SSN |
| CP54G | Different name/ID number on return; need more information | Name/SSN |
| CP54Q | Need updated name/SSN; no response to previous notice | Name/SSN |
| CP560A | Child assigned an Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN) | ATIN |
| CP560B | One-year extension granted for child’s ATIN | ATIN |
| CP561A | Child’s ATIN expires in 3 months | ATIN |
| CP561B | Extension for child’s ATIN expires in 3 months | ATIN |
| CP561C | Child’s ATIN has expired | ATIN |
| CP562A | Incomplete Form W-7A; need more information | ATIN |
| CP562C | Need more information to process extension for child’s ATIN | ATIN |
| CP563 | Need more information to process Form W-7A | ATIN |
| CP565 | Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) assigned | ITIN |
| CP565SP | ITIN assigned (Spanish) | ITIN |
| CP566 | Need more information to process ITIN application | ITIN |
| CP567 | ITIN application rejected | ITIN |
| CP57 | Penalty assessed for insufficient funds | Penalty |
| CP59 | No record of prior tax return(s) being filed | Filing |
| CP60 | Payment erroneously applied; removed from account | Payment |
| CP601 | Balance due (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP603 | Unpaid balance, no response (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP604 | Unpaid balance; levy/state tax offset warning (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP615I | Past-due amount for prior year taxes; action needed (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP616 | Reminder that tax payment is due (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP618I | Prior tax return(s) missing; final notice (Spanish) | Filing |
| CP62 | Payment applied to account | Payment |
| CP621 | Installment agreement payment overdue (Spanish) | Installment agreement |
| CP623 | Installment agreement defaulted; intent to terminate and levy (Spanish) | Levy |
| CP63 | Holding refund; unfiled returns expected to result in taxes owed | Refund |
| CP701B | IRS needs more information to process tax return (Spanish) | Identity theft |
| CP701C | Account flagged for identity theft (Spanish) | Identity theft |
| CP701S | Identity theft claim received; refund or more information forthcoming (Spanish) | Identity theft |
| CP71 | Reminder of unpaid balance, penalty, and interest owed | Balance due |
| CP711 | Balance due from changes on tax return (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP712 | Changes made to correct math error (Spanish) | Return error |
| CP713 | Changes made to correct math error; zero balance (Spanish) | Zero balance |
| CP714 | Past-due amount owed (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP71A | Reminder of outstanding balance; payment needed to avoid additional penalties | Balance due |
| CP71C | Tax, penalty, and interest still owed; payment needed to avoid further penalties | Balance due |
| CP71D | Reminder notice of tax, penalty, and interest owed | Balance due |
| CP71H | Reminder notice of unpaid SRP balance | Balance due |
| CP72 | Frivolous return identified; no basis in tax law | Frivolous return |
| CP721 | Changes requested for IRA contributions result in a balance due (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP721B | Changes requested result in a refund; refund issued in 2–3 weeks (Spanish) | Refund |
| CP721C | Changes requested result in zero balance (Spanish) | Zero balance |
| CP721E | Changes requested result in taxes owed (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP721I | Changes to return result in additional taxes owed for IRA contributions (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP722 | Changes requested result in taxes owed (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP722E | Changes from recent audit result in taxes owed (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP722I | Changes to return result in additional taxes owed for IRA contributions (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP74 | Form 8862 received; eligibility confirmed for certain tax credits | EITC |
| CP749 | All or part of refund used to pay tax debt (Spanish) | Payment |
| CP75 | Audit of return; further documentation required; may affect EITC and/or dependent credits | EITC |
| CP759 | No record of prior tax return(s) being filed (Spanish) | Filing |
| CP75A | Audit of return; need to verify EITC, exemptions, and filing status | EITC |
| CP75C | Banned from claiming EITC due to past violation | EITC |
| CP75D | Audit of return; need to verify income and withholding; may affect EITC, etc. | EITC |
| CP76 | EITC allowed; refund expected within 8 weeks (if no other tax debts) | EITC |
| CP77 | Intent to levy assets; notice of CDP hearing rights | Levy |
| CP771 | Balance due reminder — tax, penalties, and interest (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP772 | Balance due reminder — tax, penalties, and interest (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP773 | Balance due reminder — tax, penalties, and interest (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP774 | Balance due reminder — tax, penalties, and interest (Spanish) | Balance due |
| CP79 | EITC denied; cannot be claimed until eligibility proven | EITC |
| CP79A | EITC denied due to recklessness; ineligible for 2 years | EITC |
| CP79B | EITC denied due to fraud; ineligible for 10 years | EITC |
| CP80 | Payments/credits applied to account, but return is missing | Filing |
| CP81 | Missing return for specific year, refund claim deadline approaching | Filing |
| CP87A | Duplicate dependent or qualifying child claimed on another return | Duplicate TIN |
| CP87B | Claimed exemption while being claimed as dependent exemption on another return | Duplicate TIN |
| CP87C | Same dependent claimed on another return (income exceeds exemption) | Duplicate TIN |
| CP87D | Dependent on your return also filed jointly; may not qualify for EITC | Duplicate TIN |
| CP88 | Holding refund; unfiled returns and expected tax liability | Filing |
| CP90 | Intent to levy assets; notice of CDP hearing rights | Levy |
| CP90C | Levy action taken on assets; notice of CDP hearing rights | Levy |
| CP91 | Intent to levy up to 15% of Social Security benefits; notice of CDP hearing rights | Levy |
| CP92 | Levy action taken on state tax refund; notice of CDP hearing rights | Levy |
| CP94 | Restitution-based assessment made per court order | Levy |
| Letter 0012C | Information needed to reconcile advance payments of Premium Tax Credit (PTC) | General |
| Letter 0484C | Collection Information Statement requested (433F/433D) or unable to pay/transfer | General |
| Letter 0549C | Balance due on account paid | General |
| Letter 0681C | Proposal to pay accepted | General |
| Letter 0757C | Installment privilege terminated | General |
| Letter 1961C | Installment agreement for direct debit 433-D | General |
| Letter 1962C | Installment agreement granted/revised | General |
| Letter 2257C | Total balance due | General |
| Letter 2271C | Installment agreement revisions for direct debit | General |
| Letter 2272C | Installment agreement cannot be considered due to unpaid balance | General |
| Letter 2273C | Installment agreement granted; terms explained | General |
| Letter 2357C | Abatement of penalties and interest | General |
| Letter 2603C | Installment agreement granted; notice of federal tax lien | General |
| Letter 2604C | Pre-assessed installment agreement | General |
| Letter 2761C | Request for combat zone service dates | General |
| Letter 2789C | Taxpayer response to reminder of balance due | General |
| Letter 2800C | Incorrect W-4 (withholding allowance) | General |
| Letter 2801C | Not entitled to claim exempt status | General |
| Letter 2802C | Withholding does not comply with IRS guidelines | General |
| Letter 2840C | Confirmation of direct debit installment agreement (DDIA) | General |
| Letter 3030C | Balance due explained; tax and Interest not paid | General |
| Letter 3127C | Revision or reinstatement of installment agreement | General |
| Letter 3217C | Installment agreement accepted; terms explained | General |
| Letter 4281-A | Get Transcript incident; notice of unsuccessful attempt to use taxpayer SSN to access transcripts | General |
| Letter 4281-B | Get Transcript incident; notice of successful attempt to use taxpayer SSN to access transcripts | General |
| Letter 4281-C | Notice of data loss/disclosure to potentially impacted individuals | General |
| Letter 4281-E | Get Transcript incident; primary taxpayer notified of possible SSN disclosure of others on return | General |
| Letter 4281-F | Get Transcript incident; notification for individuals indirectly related to the accessed account | General |
| Letter 4281-G | Get Transcript incident; notification that taxpayer’s SSN was used to access transcripts | General |
| Letter 4458C | Monthly installment payment not received | General |
| Letter 4883C | Return received; more information needed to process | General |
| Letter 5071C | Return received; identity verification needed to process | Identity theft |
| Letter 5591 | PTC non-filer letter | General |
| Letter 5591A | PTC non-filer letter | General |
| Letter 5596 | PTC non-filer letter | General |
| Letter 5598 | Return filed without attaching Form 8962; need to file amended return | General |
| Letter 5599 | Return filed without attaching Form 8962; need to file amended return | General |
| Letter 5600C | May have overpaid SRP on 2014 return | General |
| Letter 5821 | Need to renew ITIN to file a return | General |
| Letter 5821 (SP) | Need to renew ITIN to file a return (Spanish) | General |
| Letter 5858 | Form 1095-A received; must reconcile PTC | General |
| Letter 5858 (SP) | Form 1095-A received; must reconcile PTC (Spanish) | General |
| Letter 5862 | Form 1095-A received; must reconcile PTC | General |
| Letter 5862 (SP) | Form 1095-A received; must reconcile PTC (Spanish) | General |
| LP47 | Request for assistance in locating taxpayer (for employers) | Address update |
| LP59 | Previous levy notice received; no response | Levy |
| LP61 | Need information about current or former employee | Taxpayer info request |
| LP62 | Information request about taxpayer to resolve tax matter | Taxpayer info request |
| LP64 | Request for assistance in locating taxpayer | Locate taxpayer |
| LP68 | Release of levy notice | Levy |
| LT11 | Notice of intent to levy for overdue taxes | Levy |
| LT14 | Past-due taxes; unable to reach taxpayer | Balance due |
| LT16 | Enforcement action may be taken to collect taxes | Balance due |
| LT18 | No response to previous requests for overdue return | Balance due |
| LT24 | Received installment agreement offer; more information needed | Balance due |
| LT26 | No response to previously requested information for a specific tax period | Information request |
| LT27 | Need to file Form 433-F for payment plan | Installment agreement |
| LT33 | Payment received, but outstanding balance remains | Balance due |
| LT39 | Legal requirement to issue reminder of overdue taxes | Balance due |
| LT40 | Trying to collect taxes; may contact others to verify info | Balance due |
| LT41 | Trying to collect unfiled returns or SRP; may contact others to verify info | Balance due |
| LT73 | Notice of levy to collect unpaid federal employment taxes | Employment tax |
| LT75 | Federal tax unpaid; levy issued to collect | Levy |
| SP64 | Request for assistance in locating taxpayer (Spanish) | Locate taxpayer |
| ST11 | Notice of intent to levy for overdue taxes (Spanish) | Levy |
| ST14 | Balance due on unpaid taxes (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST16 | Enforcement action may be taken to collect taxes (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST18 | Enforcement action may be taken to collect taxes (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST24 | Received installment agreement offer; more information needed (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST26 | No response to previously requested information for a specific tax period (Spanish) | Information request |
| ST27 | Need to file Form 433-F for payment plan (Spanish) | Installment agreement |
| ST33 | Payment received, but outstanding balance remains (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST39 | Legal requirement to issue reminder of overdue taxes (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST40 | Trying to collect taxes; may contact others to verify info (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST41 | Trying to collect unfiled returns or SRP; may contact others to verify info (Spanish) | Balance due |
| ST73 | Notice of levy to collect unpaid federal employment taxes (Spanish) | Employment tax |
| ST75 | Federal tax unpaid; levy issued to collect (Spanish) | Levy |
Disclaimer: This post provides general information and should not be considered tax advice. Consult a qualified tax professional for guidance tailored to your specific tax situation.


